Clinical signs.
At early age children in conditions of a massive tubercular infection the primary tubercular complex proceeds for pneumonic type with an extensive damage of intrathoracic lymphatic nodes. The development of disease is characterized by sharp beginning with a high fever and increase of temperature till 39-40 C, complaints of cough, dry or with allocation mucous sputum, pain in thorax.
Pneumonia (lobe or segmental) accepts diffused character that depends from hyperallergic reactions and unfinished differential process in lungs of the kids. At children of the senior age the small primary focuses in lungs are formed, and among some of them the various complications of the primary tubercular complex come to light. At objective examination of the child it are found out enlarged lymphatic nodes (cervical, axillary’s) dense, mobile, without perifocal inflammation in surrounded tissues. At large lung focus the backlog in the action of breath of one half of thorax is observed. Above the focus dullness of percussion tone, small bubbly moist rales are listened. At small lung focuses the physical changes are not present.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis could be found out in flush waters of bronchi, stomach, which get into flash waters not only from infiltrative pneumonic focuses in lungs, but also from specific changes in bronchi.
The examination of blood reveals moderate leucocytosis with shift of the neutrophyl formula to the left, eosinopenia, monopenia and acceleration of ESR.
Diagnostics.
For making the diagnosis of primary complex the anamnesis has large importance with indications of contacts with patient having mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum and positive tuberculin tests. The virage (conversion) of tuberculin tests is especially valuable which at a fresh and active primary complex is shown by hyperallergic reactions. It is very important examination of the sputum, flash waters from bronchi and stomach on presence of mycobacterium tuberculosis. X-ray examinations can reveal fresh focuses in lungs with accompanying adenitis.
The complications of primary tubercular complex.
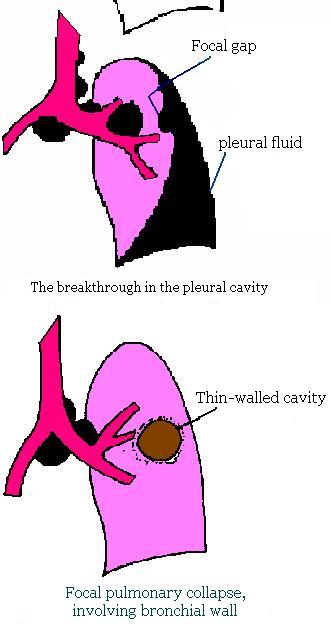 The complications of primary tubercular complex development cause progressing of the process: formation of destruction in lung tissue, involvement in process of the neighboring organs (bronchi, pleura), and occurrence of lymphatic and hematogenic disseminations.
The complications of primary tubercular complex development cause progressing of the process: formation of destruction in lung tissue, involvement in process of the neighboring organs (bronchi, pleura), and occurrence of lymphatic and hematogenic disseminations.
Differential diagnosis. Making the differential diagnosis of primary tubercular complex with nonspecific pneumonia is not difficult. The non-specific pneumonia onset is usually sharp and quick, rough, is accompanied with fever, temperature increase up to 39-40 C. On lips the herpes could be found out. Objectively in nonspecific pneumonia stetoacoustic data are rich: intensive dullness, amplification of voice vibrations, bronchial breath with rich of rattles. The blood is usually revealed high leucocytosis (15000-20000), neutrophilia. Non-specific pneumonia usually proceeds with a rough clinical picture and for the short period come to an end by crisis.
At the primary tubercular complex general condition of the patient usually rather good, tuberculin tests are strongly positive, МВТ are presented in sputum, paraspecific scleritis, slow reverse dynamics of process.
The chronic primary tuberculosis.
The disease gets chronic wavy course at late diagnosis of primary tuberculosis and insufficient treatment. The chronic forms of primary tuberculosis represent a progressing defeat of lymphatic nodes with massive caseous necrosis, not inclined to complete healing. Казеозный; The process of caseation in lymphatic nodes is a source of aggravations and lymphatic and hematogenic disseminations. The clinical forms of chronic primary tuberculosis are characterized by diverse symptoms with defects of various organs in combination with symptoms of tubercular intoxication. The periodic aggravations can be shown as penetrations of caseous masses from mediastinum lymphatic nodes into bronchial system, involvement into specific process serous membranes and so on.
The untypical forms of the chronically primary tuberculosis proceed under masks of other diseases. The following masks are recognized: nervous–dystrophic, endocrine, cardio-vascular, blood formation, polyserosis, and hepatic, gastrointestinal, renal. Such masks now meet seldom. In time revealing and the treatment of tuberculosis prevent development of the chronic progressing forms of primary tuberculosis.
Prevention and treatment of primary tuberculosis.
The important role in prevention of primary tuberculosis belongs to BCG vaccination and revaccination. The certain importance has chemoprophylaxis of primary tuberculosis at the persons with the recent virage of tuberculin tests, and also in conditions of contact with MBT sputum positive patients.
At treatment of primary tuberculosis first of all the methods promoting decrease of increased sensitivity are needed and restoration of normal function of nervous system and desintoxication of organism. The treatment should be complex, long, with correct organization of a hygiene-dietary mode. The long stay of the patients on air at any time of year is necessary, thus it is impossible to subject their long sun light irradiation, being the irritating factor for sensibilized organism.
Doses of antibacterial drugs for children count per 1 kg of weight. The treatment should be directed on achieving complete dissolution of infiltrations, condensation or calcification of the focuses, elimination of functional infringements.